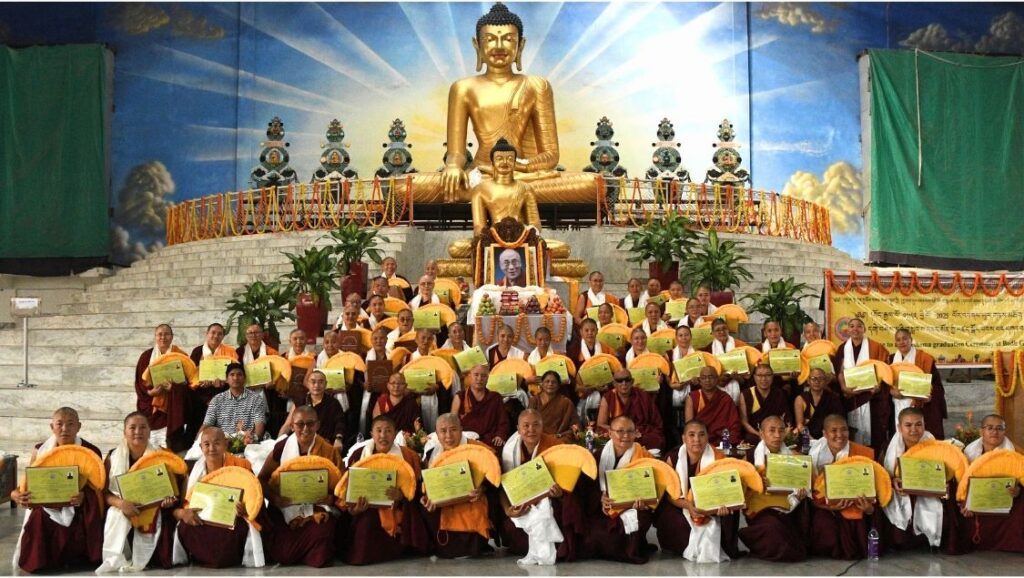
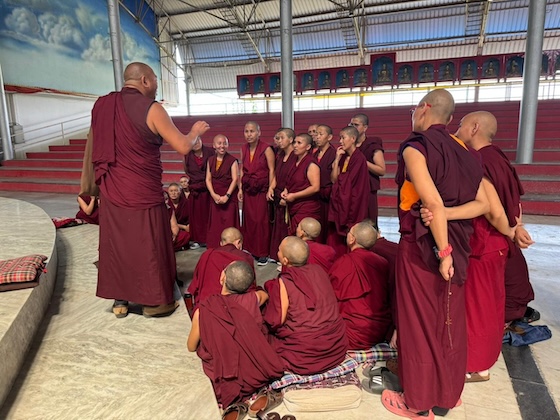
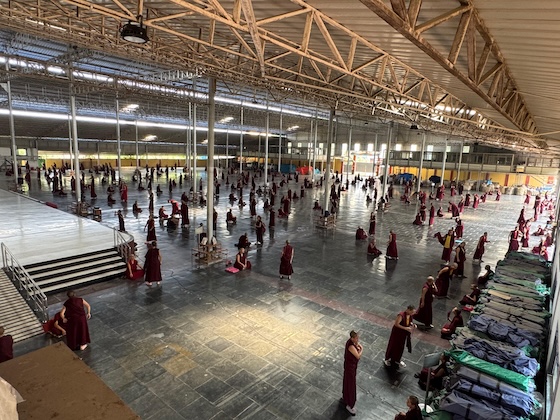
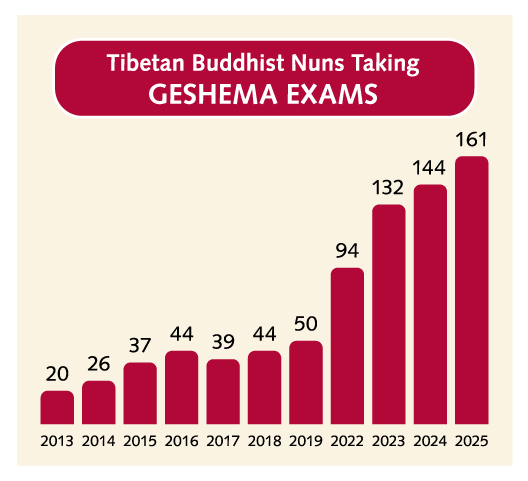
Traditionally, Buddhist nuns have not had the same access to education as monks, but your generosity is changing that. We would like to extend a special thank you to everyone who sponsors a nun.
Here are photos showing recent academic competitions at Shugsep Nunnery and Institute, a nunnery built and fully supported by donors to the Tibetan Nuns Project.
Shugsep Annual Tibetan Grammar Competition Day
The nuns at Shugsep Nunnery held their annual Tibetan grammar competition in November. The preservation of Tibet’s unique language and culture remains one of the most critical areas of focus for Tibetans, both inside Tibet and in exile.
Events like this enhance the nuns’ knowledge of various subjects, boost their confidence, encourage creativity, strengthen their communication skills, and provide the nuns with valuable practice in expressing their ideas clearly.
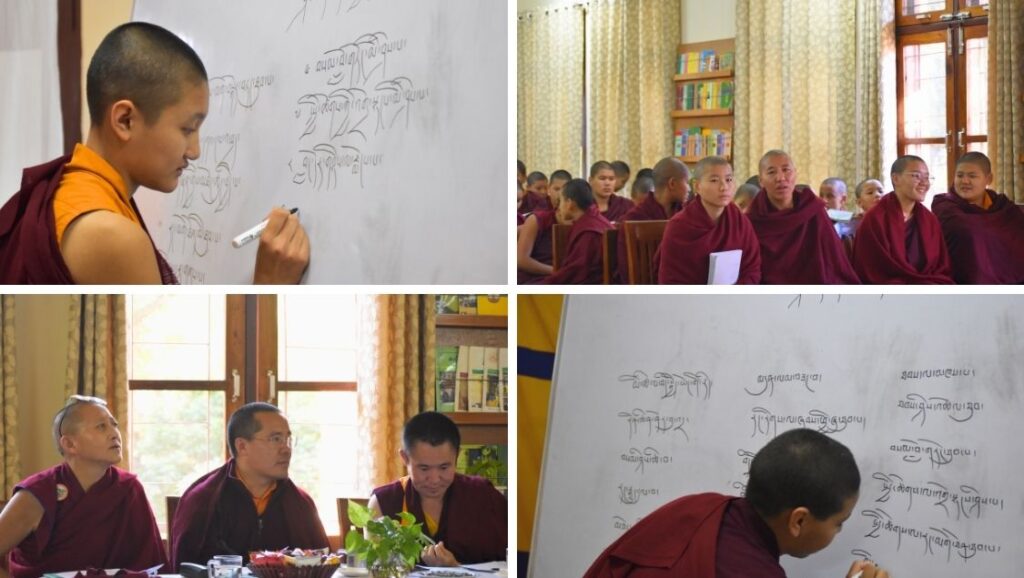

The annual Tibetan grammar competition at Shugsep Nunnery. Tibet has its own language, including a unique alphabet and various written forms. Tibetan calligraphy is beautiful, and there are numerous Tibetan writing styles.
These types of competitions are held in various subjects and topics, depending on the class level. They help the nuns become more comfortable speaking and writing in front of others, and they build a healthy sense of discipline and motivation.
The idea for this competition originated at a staff meeting, when some teachers suggested holding regular activities to enhance the nuns’ overall knowledge and, most importantly, to help build their confidence.
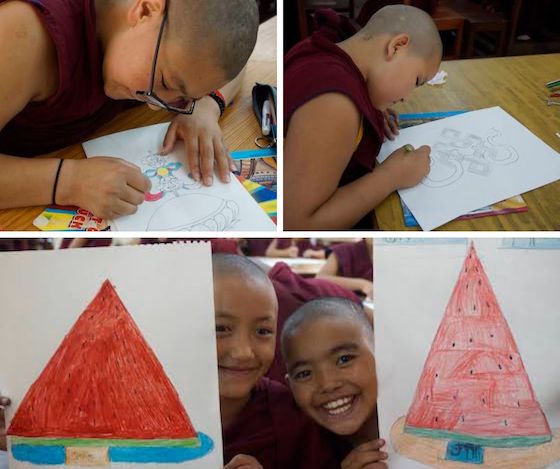
On November 8th, the nunnnery held a Tibetan Language Skills competition that included poem writing and application for the higher grades. The competition had questions such as “Write down five different proverbs,” “What are the elements needed to complete a composition?” and other Tibetan grammar questions.

The Tibetan alphabet has 30 characters or letters and four vowels. Like English, it is written from left to right in horizontal lines. Tibetan writing may be broadly divided into two types: “headed”, called Uchen, and “headless”, called Umeh. These two forms of Tibetan script correspond roughly to printed and cursive writing.
For the younger students, the activities included a reading competition and a spelling exam, where students were asked to write specific names or words.
Around 50 nuns participated, except for those who had already completed their Loponma degrees, roughly equivalent to a master’s degree. A panel of teachers scored the competitions and awarded prizes for 1st, 2nd, and 3rd place.
Annual English Competition and The Alchemist
Here are some delightful photos taken by the nuns during the annual English competition held on December 6th at Shugsep. The event took place in the presence of Khenpo-la (the head of the nunnery) and all the teachers. They watched a lovely drama performed by the children and viewed many beautiful drawings created by the junior students.
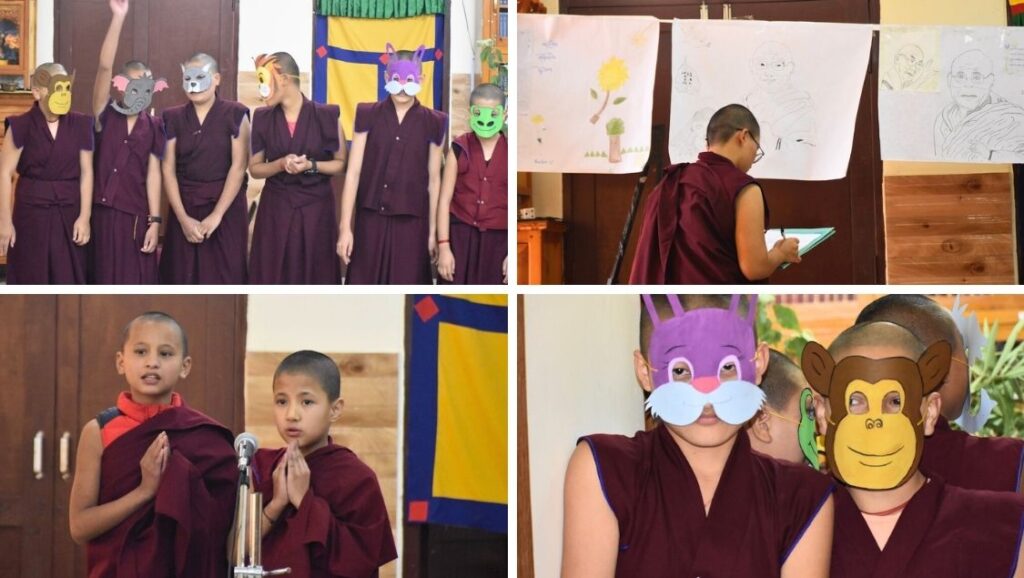

It’s never easy standing up in front of your classmates, all your teachers, and your principal. It’s even more challenging when you have to speak a foreign language. Congratulations to all the nuns who took part in the annual English competition. The young nuns performed a drama.
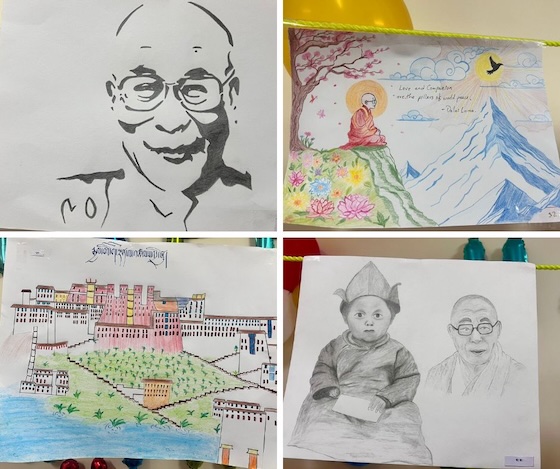
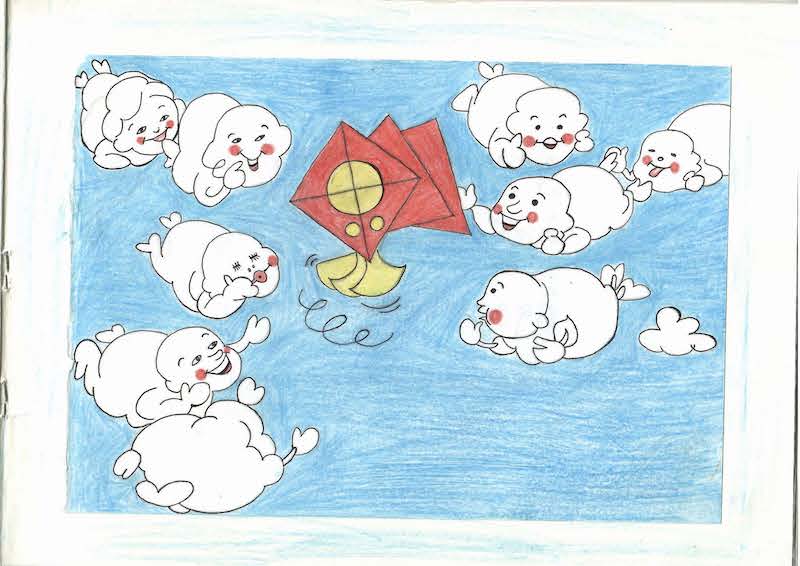
The junior students created many beautiful drawings to reflect daily life at the nunnery and also the Year of Compassion, honouring the 90th birthday of His Holiness the Dalai Lama.
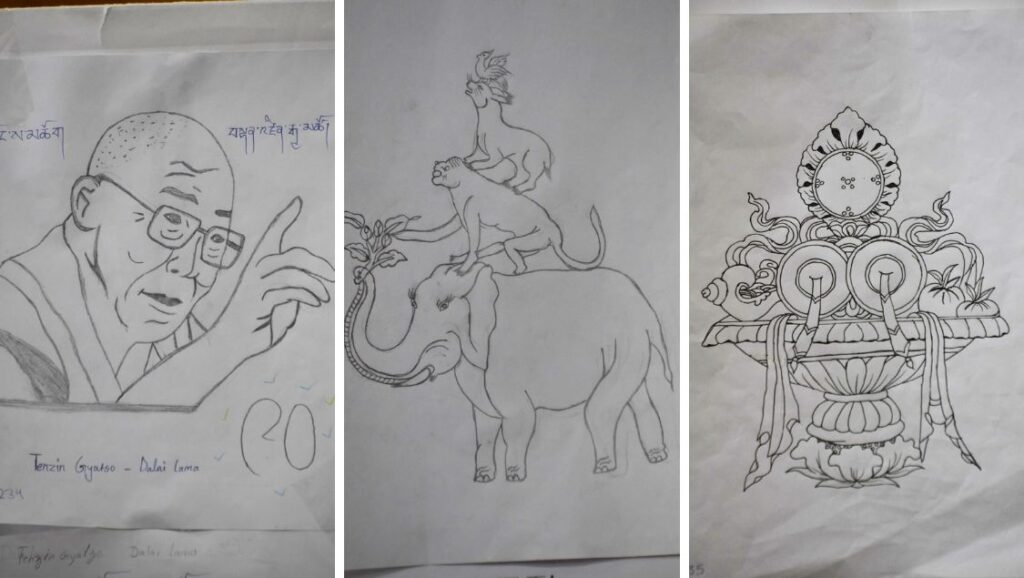

Here are some of the drawings by the junior nuns at Shugsep. The nuns had to describe the images in English to the assembled crowd. This builds confidence and skills in English and public speaking. The picture on the left honors His Holiness the Dalai Lama’s 90th birthday, and the middle picture is the “Four Harmonious Friends”, one of the Jataka tales of Buddhist mythology.
As part of the competition, the senior nuns wrote English poems and notices.
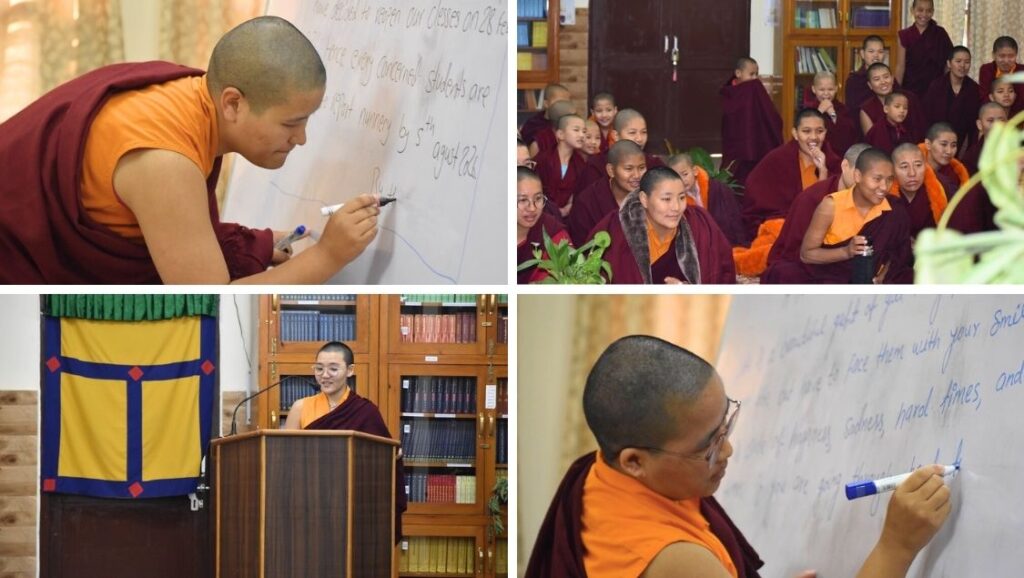

Shugsep is now home to about 100 nuns. The senior nuns are writing in front of their classmates and teachers as part of the annual English competition.
The nuns also spoke about the famous novel The Alchemist by Brazilian writer Paulo Coelho. The book’s main theme is about finding one’s destiny.
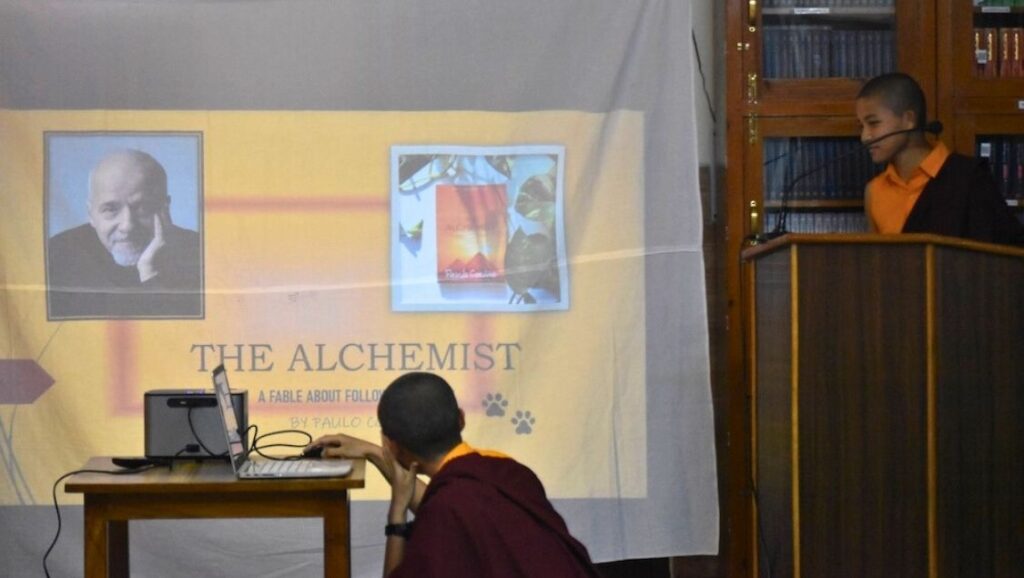

In this photo, two nuns are explaining the introduction of The Alchemist to the audience, highlighting the book’s strong and important vocabulary and philosophical concepts.
The Tibetan Nuns Project aims to elevate the educational standards and the position of women. As TNP’s Founding Director and Special Advisor Rinchen Khando Choegyal has said, “Educating women is powerful… It’s about enabling the nuns to be teachers in their own right and to take on leadership roles at a critical time in our nation’s history.”
Thank you for helping the nuns on their path!